Following the arrest of Telegram founder Pavel Durov in France last summer, some positive changes were reported. The criminal probe is not centered on piracy, but Telegram appeared more responsive. Some reported that the speed at which takedown requests were processed, went from more than 24 hours to less than 20 minutes, for example.
In addition, Telegram updated its terms of service and privacy policy to clarify that, going forward, personal details of alleged infringers, including their IP addresses, would be handed over in response to valid legal requests.
This stricter policy was evident to outsiders as well. Telegram removed accounts of piracy associated websites and services, after initially leaving these untouched for years. That included the official Z-Library channel, which had more than half a million subscribers at its peak.
Although Z-Library’s communication channel didn’t directly link to pirated books, it served as a key information hub, providing updates on new features and access methods. That was enough to warrant a permanent suspension last month.
The Telegram ban was a setback for Z-Library, but the shadow library wasted no time creating a new account and regaining tens of thousands of subscribers. Progress ground to a halt last weekend when the ‘new’ @zlibrary_news account was also suspended for copyright infringement.
“The channel is unavailable due to copyright infringement,” Telegram reports.

In addition to the main communication channel, one of the most used Z-Library download bots on Telegram was also taken offline. The @1lib account had more than 20,000 monthly users, who presumably used it as a handy tool to download books for free.
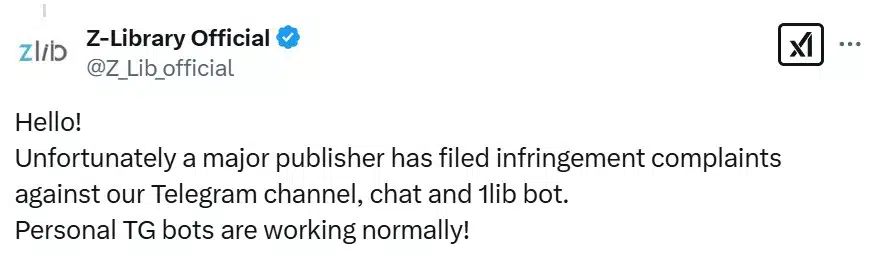
According to a Z-Library representative posting on X, Telegram took action in response to complaints from a major publisher. Many other ‘personal’ bots are unaffected and remain online for the time being.


How do you discover providers on simplex?